Robots aim to replace humans in tasks where they are less effective, thus lowering risks associated with dangerous situations and speeding production.
Robot performance relies heavily on its tight integration between physical body and algorithms, and their abilities. They must be capable of navigating, mapping new environments, recognising objects and learning from their environment.
Industrial Robots
Modern manufacturing facilities use industrial robots extensively, helping improve productivity, efficiency and product quality across numerous industries while becoming more versatile and customizable over time.
Robots can make quick work of dirty, dangerous or boring tasks that would exhaust humans – work that requires precision only robots can provide. Programmable to work around the clock without breaks required and with materials of various kinds and environments in mind. Plus they free employees up for more important tasks!
While robotics has existed since ancient times, major breakthroughs did not become evident until the 20th century due to advancements in digital electronic circuitry that enabled robots to utilize computers for movement control with more consistency and accuracy than before.
Moore’s Law and other technological innovations have since enabled robots to become smaller, faster and more powerful – not only making them more effective but also making them more available and accessible – and industrial robots are now capable of handling everything from food processing and assembly tasks all the way up to surgery procedures.
Automotive was an early adopter of robot technology to streamline various manufacturing processes and increase productivity, quality, safety and production costs simultaneously. Estimates suggest this breakthrough has increased productivity, quality and safety while simultaneously decreasing production costs.
Robots have long been an integral component of electronics manufacturing processes, performing crucial tasks such as component placement and soldering. Some manufacturers rely on highly specialized robots like Delta or Cobots that are designed to work alongside human operators.
Many manufacturers are now providing industrial robot rentals on a pay-per-use basis to other businesses, which is particularly advantageous for small and mid-sized manufacturers who cannot afford upfront capital costs and ongoing maintenance expenses associated with owning their own systems.
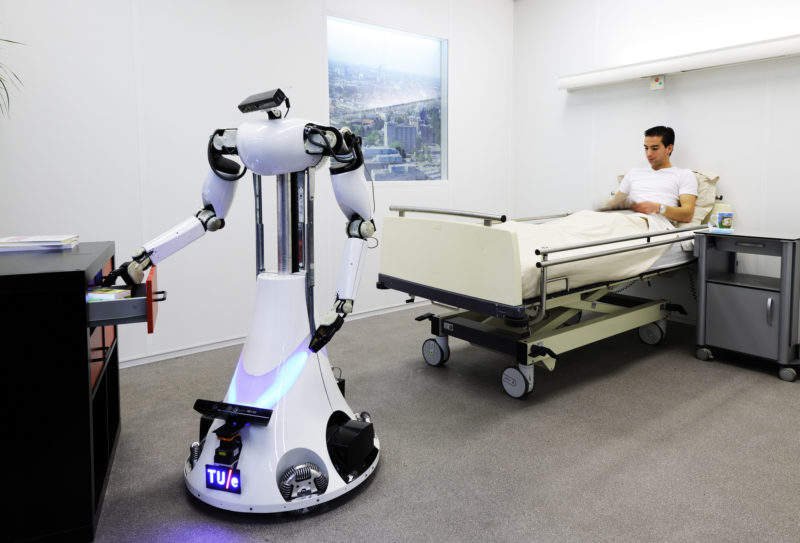
Medical Robots
Medical robots are technical apparatuses used in medicine to perform mechanical work or assist with tasks. Ranging from simple machines to multi-armed wonderbots that assist doctors during more precise surgical operations, medical robots do not replace human employees but simply enhance them by performing certain tasks more quickly and precisely than humans could. Despite what may be depicted by certain fictional depictions, these medical robots do not replace humans but simply augment them by performing certain tasks quicker and with greater precision than humans can.
One of the greatest advances in robotic technology has been multi-armed medical robots that can perform precise surgeries without human error. These robots use sensors that detect their surroundings and a computer program to execute commands more precisely than humans would, enabling them to complete tasks more precisely than humans ever could.
Medical robots are typically created to assist surgeons during surgical procedures, freeing up their hands to focus on other tasks. For instance, spine surgery typically involves several lengthy steps that involve aligning instruments and drilling as well as constant checking for alignment; with help of a robot these steps can be divided into two separate steps, potentially decreasing surgeon workload and potentially shortening procedure times.
Medical robots can also assist in more routine healthcare duties, like dispersing medications and lab samples throughout the hospital. US robotics company Aethon has recently developed a mobile robot capable of automating this process and thereby cutting costs while decreasing errors.
Furthermore, robotic exoskeletons based on Iron Man technology are being utilized to assist paralyzed patients to walk again – further demonstrating how robots are not only beneficial in military settings but can improve lives too.
As machine learning, data analytics, and computer vision continue to advance, medical robots will become ever more advanced – eventually replacing some of the routine healthcare tasks requiring human interaction with these sophisticated technologies. Their use could result in shorter wait times, less-invasive procedures and even better diagnoses.
Collaborative Robots
Robots have long been an indispensable component of industrial production and manufacturing. From welding and assembly, to inspecting and testing, these machines perform work that would otherwise be difficult for humans to complete safely and quickly. Furthermore, many workplace environments present too great a danger for workers that would necessitate human exposure; examples include high heat environments or working at extremely tall heights where exposure may prove fatal; robots must therefore remain distant from human workers and be shut off if they get too close.
Cobots (collaborative robots) can safely integrate themselves into any workplace environment by connecting and communicating with its operator through sensors and an internal system that ensures no human is injured by its movements. With force limits that reduce potential collisions and smooth designs that minimize collision risks, collaborative robots help businesses reduce operating costs while increasing productivity.
Collaborative robots are more accessible to non-expert users than their industrial robotic counterparts, which require experienced technicians for programming and control. Collaborative robots often referred to as low-code or no-code due to using intuitive programming solutions that make them simpler for entry level technicians to understand and operate.
One major distinction between collaborative and non-collaborative robots lies in their ability to complete tasks without needing vision systems or safety barriers – essential requirements in an industrial setting. Furthermore, these collaborative robots can be reprogrammed more rapidly due to not requiring such complex programming environments like traditional industrial ones do.
As scientists work to discover new techniques for improving robot technology, there has been an upsurge in popularity of collaborative robots as part of workplace environments. These types of robots offer many similar functions as traditional industrial ones; yet have additional advantages that make them suitable for smaller companies and industries.
First and foremost, cobots eliminate the need for large and expensive visual systems and safety barriers, providing cost-effective and time-saving benefits. Furthermore, cobots are more reliable as they don’t blindly perform tasks; rather they store visual data using AI for analysis; if something doesn’t look quite right (such as food not meeting quality control standards), cobots will automatically bypass it, saving time, resources, and assuring quality control of products.
Robots in Space
Development, creation and use of robotic technology has evolved from sci-fi fantasies into an industry in recent decades. From Mars rovers exploring its surface to humanoid robots performing maintenance duties aboard space stations, robotic technology is now used in all conceivable tasks from law enforcement assistance, surgical procedure streamlining to rescue missions – making its presence felt everywhere from Earth’s harsh environments to outer space stations!
As more emphasis is put on robotics with more diverse abilities and complex functionality, their possibilities for revolutionizing our understanding of our place within nature are unbounded. These autonomous machines may even transform how we view reality itself.
Sensor technology advances and the ongoing advances in machine learning and artificial intelligence will enable robots to become smarter, more versatile, and quicker at responding quickly to unexpected situations. Smaller robots, sustainability-minded designs, and regulatory considerations will also play a key role in shaping this field’s future.
As robots can undertake various tasks without direct supervision, they make ideal candidates for missions in outer space. Their resilience in extreme conditions makes them work tirelessly for extended periods, giving scientists valuable information. Robots may even explore dangerous or deadly areas for humans – protecting astronauts while gathering data from celestial bodies that would otherwise remain unknown to us.
As robots can operate efficiently in remote environments, their use enables more cost-effective space exploration compared to human missions. Since robots don’t require food or other forms of life support systems for prolonged periods, these machines can significantly lower space exploration costs while performing complex tasks more quickly while collecting massive amounts of data quickly allowing quicker scientific discoveries. In addition they can carry out maintenance repairs on spacecraft and habitats eliminating costly spacewalks reducing safety risks while saving time and reducing spacewalk risks significantly.